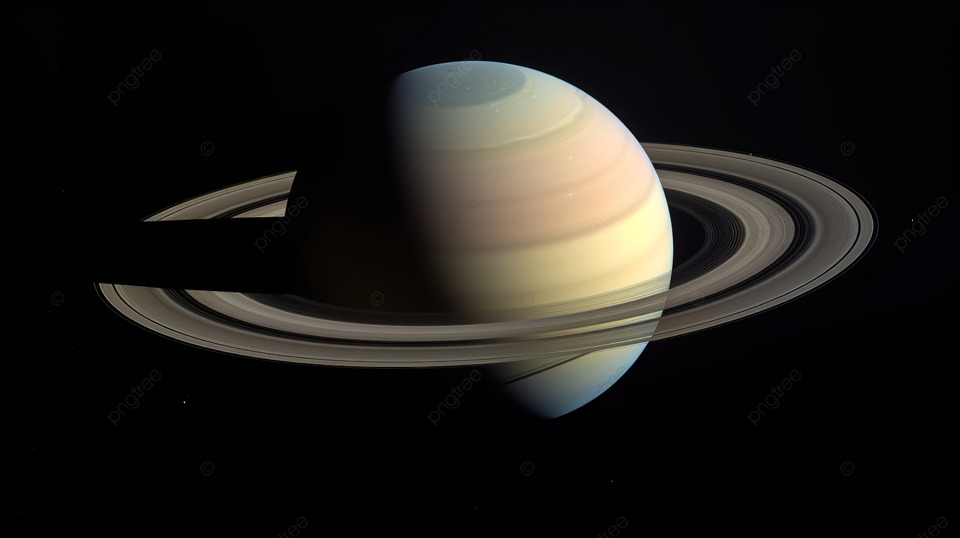

Origin And Formation
Origin and Formation
Saturn’s rings are believed to be remnants of a celestial collision or the shattered remains of a moon or icy object. The prevailing theory suggests that these rings originated billions of years ago, perhaps from a moon that ventured too close to the planet and succumbed to tidal forces, or from a comet or asteroid that disintegrated due to gravitational forces. This cosmic ballet resulted in the formation of the intricate ring system we observe today.
Composition of Particles
The mesmerizing rings of Saturn consist mainly of water ice, interspersed with smaller amounts of rock and dust. These particles vary in size, from tiny grains to sizable boulders. Their composition imparts the rings with a reflective brilliance, creating the illusion of a dazzling halo around the planet when viewed from Earth. This dynamic mix of ice and debris contributes to the rings’ intricate patterns and structures.
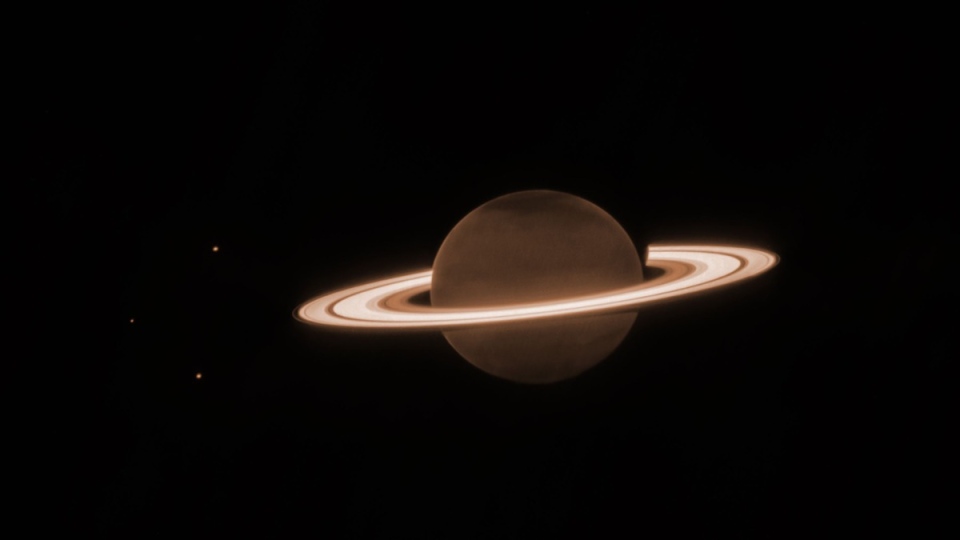

Composition Of Particles
Ring Structure
Saturn’s rings are organized into distinct, tiered structures labeled A, B, and C, with the Cassini Division serving as a gap between the A and B rings. Each of these ring divisions contains numerous ringlets, creating a tiered tapestry that spans a vast expanse around the gas giant. These ring structures result from the interplay of gravitational forces, primarily from Saturn’s moons, which exert influence and shape the intricate patterns observed within the rings.
Dynamic Evolution
Saturn’s rings are not static; they are in a state of constant flux. Collisions between ring particles, gravitational interactions with Saturn’s moons, and the influence of the planet’s magnetic field contribute to their dynamic evolution. The rings are subject to constant change, creating an ever-shifting celestial display that has fascinated astronomers and scientists studying the mechanisms behind these transformations.

Dynamic Evolution
Astronomical Significance
Saturn’s ring system serves as a natural laboratory for scientists studying astrophysical processes, planetary dynamics, and the formation of celestial bodies. By examining the composition, structure, and evolution of the rings, astronomers gain insights into the early stages of our solar system’s development and the processes that shape planetary ring systems throughout the universe.
Spectacular Views
Saturn’s rings, visible even through small telescopes, have captured the imagination of sky gazers for centuries. Their breathtaking beauty and intricate details continue to inspire both amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts. The exploration missions, such as Cassini-Huygens, have provided close-up views and detailed scientific data, deepening our understanding of these celestial wonders and ensuring that Saturn’s rings remain an enduring symbol of cosmic marvel and mystery.
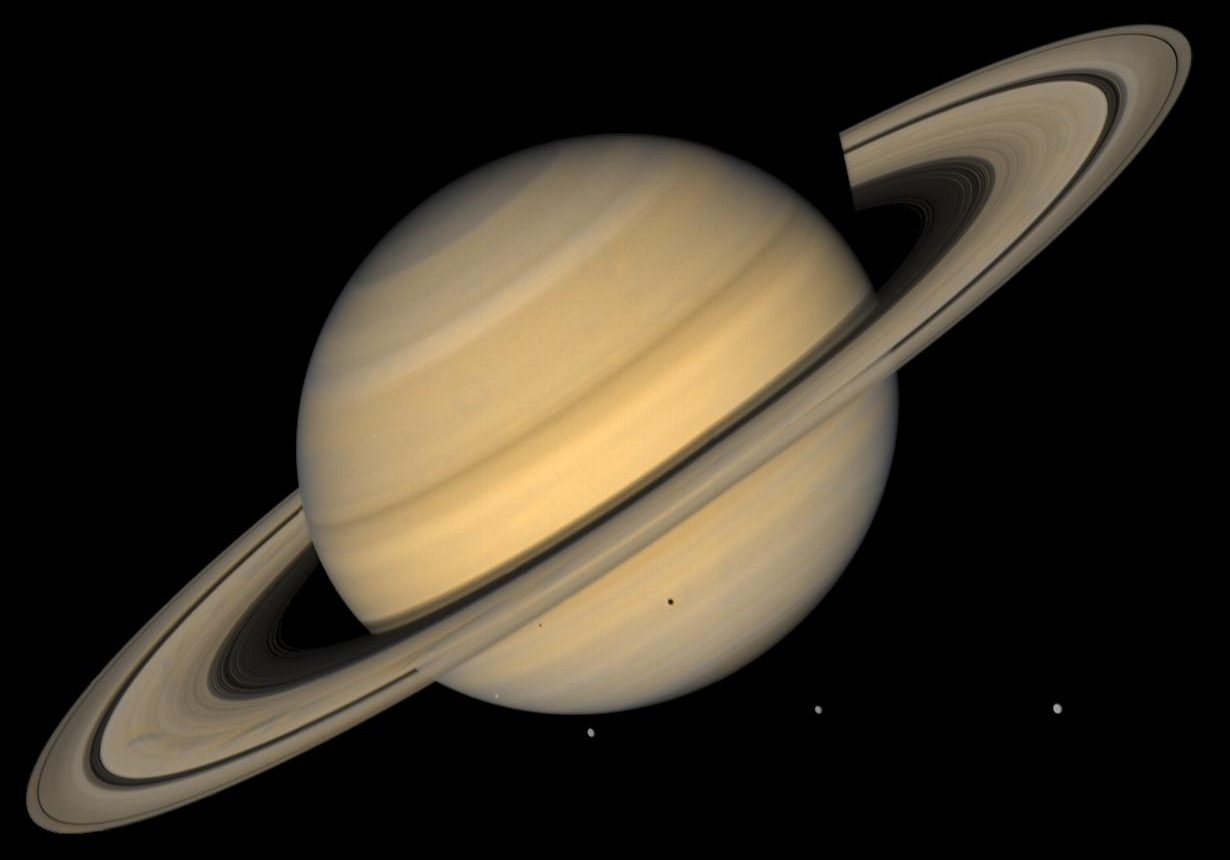
Spectacular Views








